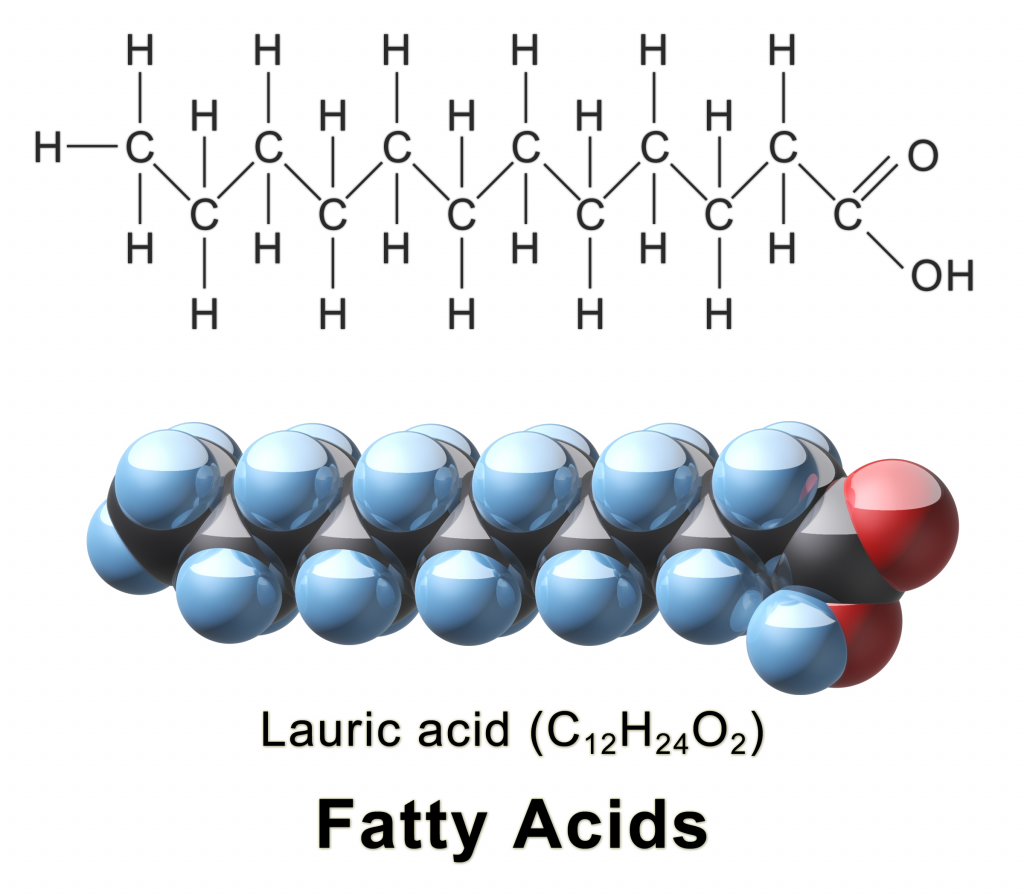
Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids . Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end with. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in.
from www.albert.io
Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end with. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Lipids AP® Biology Crash Course Review Albert.io
Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end with. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins.
From www.youtube.com
Fatty Acids & An Introduction to Lipids YouTube Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. The purpose. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From slidetodoc.com
Lecture Lipids Introduction Synthesis of Fatty Acids Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. Fatty acid, important component of. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.youtube.com
Intro to Lipids & Fatty Acids YouTube Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.scribd.com
Unit5Intro Lipids (Student Copy) PDF Lipid Fatty Acid Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end with. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lipids/ fatty acids and glycerol PowerPoint Presentation, free Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. The purpose of. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.expii.com
What Are Lipids? — Structure & Function Expii Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end with. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids.. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.researchgate.net
Scheme 1. Structural variation of fatty acids and lipids, as well as Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.youtube.com
Fatty Acids Biochemistry Classification Of Fatty Acids Biochemistry Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Lipids comprise two. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.youtube.com
Lipids (Saturated & Unsaturated fats) updated YouTube Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The purpose of. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.biologyexams4u.com
Biochemistry notes Classification of Lipids Differences between Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From slideplayer.com
AS Biology Core Principles ppt download Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats,. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Lipids OpenStax Biology 2e Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Fatty acids are. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.youtube.com
Lipids 1 Introduction to lipids, Triglycerides and Omega Fatty Acids Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lecture Lipids Introduction, Synthesis of Fatty Acids Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From chem.libretexts.org
6.1 Introduction to Lipids Chemistry LibreTexts Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins. The figure below shows three different types of molecules, a free fatty acid, a wax with an esterified fatty acid, and a. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils,. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.youtube.com
Lipids/ introduction of lipids/ Chemistry of Fatty Acids/Types of Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in. Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Introduction to Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure, function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.
From www.youtube.com
Introduction to Lipids Part 1 of 12 Fatty Acid Structure, Properties Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids Lipids comprise two separate molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) which bond together to form a triglyceride, commonly known as dietary fat. Fatty acid, important component of lipids in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these. Introduction To Fatty Acids And Lipids.